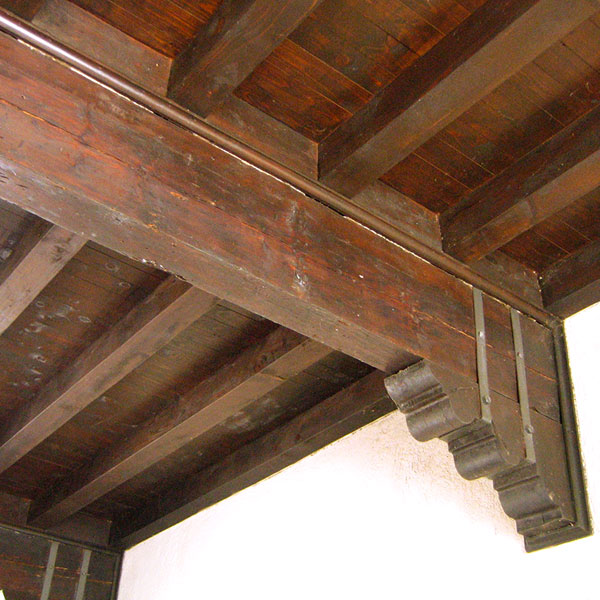
Restoration of wood floors
Existing wood floors
Old timber floors often need strengthening and stiffening as they were designed to bear moderate loads and almost always suffer from excessive deflections with respect to current requirements.
Intervening with load-bearing concrete is an optimum solution as it allows the existing floor to be reused rather than replaced, with only a modest change in the existing floor thickness.
New wood floors
New timber floors must be made with larger section beams than traditional ones if they are to be sufficiently strong and stiff. The composite wood-concrete section reduces the total thickness.
In both cases, the most convenient and easiest of solutions is to lay and connect a thin concrete slab, adequately reinforced, over the existing structure either to strengthen and stiffen existing timber floors or to allow shallower beams to be used when building new floors.
The composite wood and concrete system can also be used to make flat or pitched roof structures.
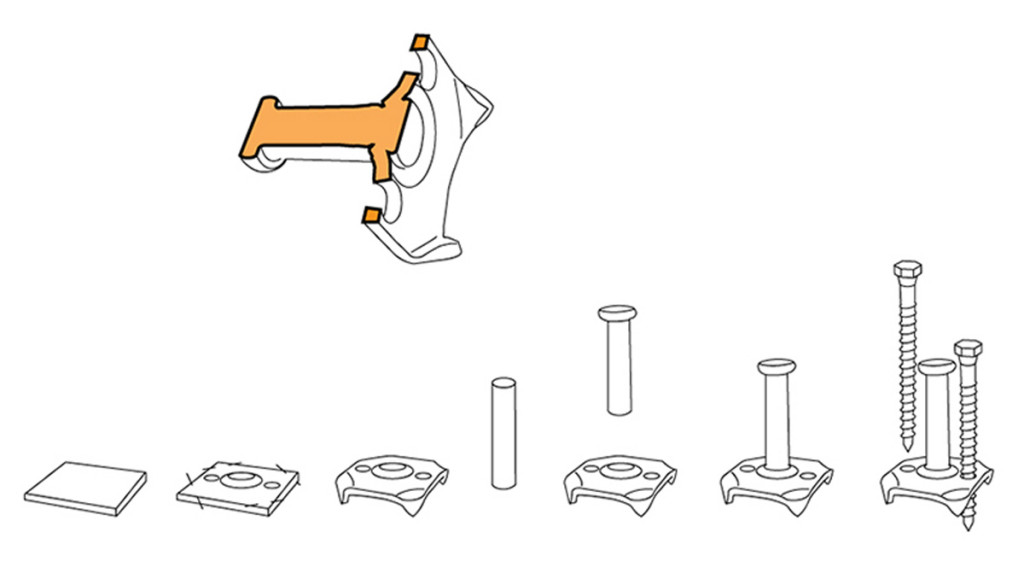
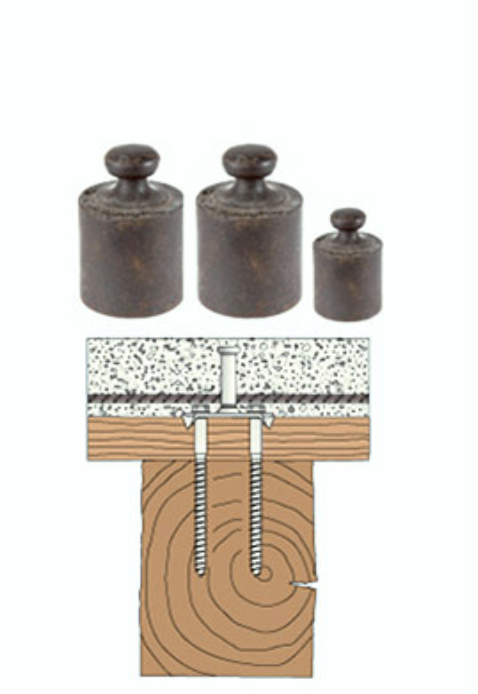
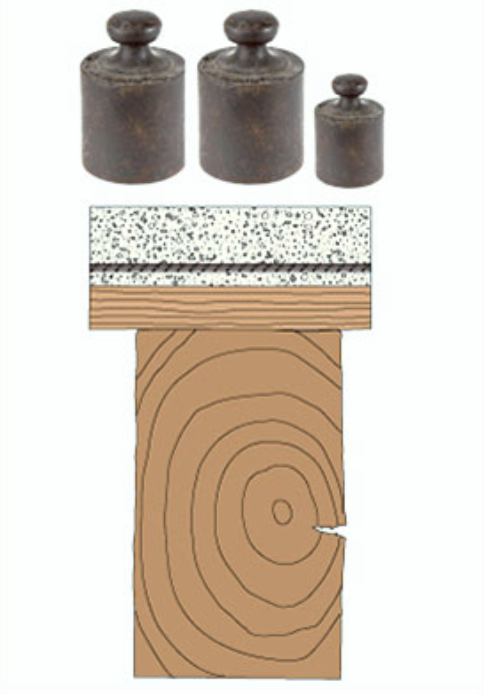
Wood floors and connectors
BEAM SEC. 12x20cm not connected carrying capacity 280kg/m²

BEAM SEC. 12x20cm not connected carrying capacity 700kg/m²

+ 150% carried weight
BEAM SEC. 12x28cm not connected carrying capacity 700kg/m²

+ 40% height
The example on the side shows the different load-bearing capacities of the beams at constant deformation. The comparison between the first image and the second is typical of the restoration of an existing wood floor. The load-bearing capacity increases significantly. The comparison between the second image and the third shows how the use of connectors can allow a significant reduction of the section of the wood beam, whilst ensuring the same load-bearing capacity.
Dowel and crampon connectors placed between the timber beams and the concrete slab make the two materials collaborate with each other, resulting in a structurally efficient structure in which the concrete is mainly under compression and the timber mainly under tension. The composite timber-concrete structure will therefore be stronger and stiffer than a simple timber structure.
There will also be an improvement in the dynamic behaviour with less vibrations, a better value of acoustic insulation and thermal inertia. The most obvious advantages for composite timber-concrete structures can be seen in a greater load-bearing capacity, a lower total height of the floor structure, greater rigidity, and improved fire resistance.